What is circadian rhythm? The circadian rhythm, often referred to as the body's internal clock, plays a pivotal role in regulating essential physiological functions, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, and overall well-being. However, modern lifestyles, irregular sleep patterns, and environmental factors can disrupt this natural rhythm, leading to various health challenges, including circadian rhythm sleep disorders. In this guide, we will explore the intricacies of circadian rhythms, delve into the signs of disruption, and provide practical insights on how to fix circadian rhythms for improved sleep quality and overall health. Whether you're grappling with insomnia, adjusting to shift work, or simply seeking a healthier sleep routine, understanding and nurturing your circadian rhythm is a key step toward achieving balance and vitality in your daily life.
What Is Circadian Rhythm
Circadian rhythms are inherent biological processes that follow an approximate 24-hour cycle, influencing the timing of various physiological and behavioral functions within the body. Governed by the body's internal clock, these rhythms are responsive to external cues, primarily the alternation between light and darkness in the environment. The master clock, known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), is situated in the brain's hypothalamus and serves as a command center that orchestrates the synchronization of various bodily functions with the natural day-night cycle.

One of the most crucial aspects of circadian rhythm sleep is its impact on the sleep-wake cycle. The body's internal clock regulates the release of melatonin, a hormone that induces drowsiness and prepares the body for sleep, in response to decreasing light levels. Conversely, exposure to light, especially in the morning, signals the body to suppress melatonin production, promoting wakefulness. Beyond sleep regulation, circadian rhythms influence processes like body temperature, hormone secretion, and metabolism, illustrating their pervasive role in maintaining overall physiological balance. Understanding and aligning with these natural rhythms can contribute significantly to improved sleep quality, alertness, and overall health.
Common Signs of Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Disruption of circadian rhythms can manifest through a range of signs that indicate an imbalance in the body's natural internal clock. Common signs include difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to insomnia or fragmented sleep patterns. Individuals may experience daytime sleepiness and fatigue, even after what might seem like a full night's sleep. Mood changes, irritability, and difficulty concentrating are also prevalent when circadian rhythms are disrupted. Additionally, disruptions can impact overall well-being, contributing to an increased susceptibility to health issues. Recognizing these signs is crucial for addressing circadian rhythm disorders promptly. Here is a concise list of common signs:

Circadian rhythm disruption occurs when the body's natural sleep-wake cycle is thrown off balance. Here are some common signs of circadian rhythm disruption:
1. Sleep Disturbances
- Difficulty Falling Asleep: Trouble initiating sleep at a regular bedtime.
- Waking Up Frequently: Waking up multiple times during the night.
- Difficulty Waking Up: Feeling groggy or tired upon waking up, even after a full night's sleep.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Excessive sleepiness during the day, often due to inadequate or poor-quality sleep at night.
2. Irregular Sleep Patterns
- Inconsistent Bedtimes: Going to bed at different times each night.
- Irregular Sleep Duration: Sleeping for widely varying amounts of time, from very short to very long periods.
- Napping at Unusual Times: Needing to nap at odd hours, especially during the day.
3. Mood Changes
- Irritability: Increased irritability or moodiness due to lack of sleep.
- Depression or Anxiety: Persistent low mood or anxiety, which can be exacerbated by poor sleep.
4. Cognitive Impairment
- Poor Concentration: Difficulty focusing on tasks, leading to decreased productivity.
- Memory Issues: Problems with short-term memory or recalling information.
- Slower Reaction Times: Reduced cognitive and physical reaction times.
5. Digestive Issues
- Appetite Changes: Changes in hunger and eating patterns, often craving sugary or high-calorie foods.
- Digestive Discomfort: Symptoms like bloating, indigestion, or constipation.
6. Physical Health Problems
- Weakened Immune System: Increased susceptibility to colds, flu, and other infections.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches or migraines.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Disruption in hormone levels, affecting metabolism, mood, and overall health.
7. Performance Issues
- Reduced Athletic Performance: Decreased physical performance, especially in athletes.
- Workplace Performance Decline: Lowered efficiency and higher error rates at work.
8. Social and Behavioral Changes
- Social Withdrawal: Reduced interest in social interactions due to fatigue or irritability.
- Increased Reliance on Stimulants: Dependence on caffeine or other stimulants to stay awake and alert.
9. Jet Lag
- Fatigue After Travel: Feeling exhausted after traveling across time zones.
- Difficulty Adjusting to New Time Zones: Struggling to adapt to the local time when traveling.
10. Shift Work Disorder
- Sleep Problems in Shift Workers: Workers who do night shifts or rotate shifts often experience circadian rhythm disruptions.
- Impact on Health: Higher risk of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes.
Addressing these signs often involves lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, exposure to natural light, and managing stress. In some cases, medical intervention or guidance from a sleep specialist may be necessary.
Factors Affecting Circadian Rhythms
Circadian rhythms are delicately balanced by a combination of internal and external factors that influence the body's internal clock. The primary external factor is exposure to light, particularly natural light during the day and the absence of light at night. Irregular sleep patterns, jet lag from travel across time zones, and shift work can significantly impact circadian rhythms. Lifestyle choices, such as inconsistent meal times, excessive screen time before bedtime, and irregular physical activity, also play a role. Hormones, particularly melatonin and cortisol, contribute to circadian regulation, with disruptions in their production affecting sleep-wake cycles. The interplay of these factors underscores the importance of adopting healthy habits and creating an environment that supports the body's natural circadian rhythm.

Tips for Resetting Circadian Rhythms
How to reset circadian rhythm involves adopting practices that realign the body's internal clock with the natural day-night cycle. One crucial strategy is to establish a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Exposure to natural light, especially in the morning, helps regulate the production of melatonin, signaling to the body that it's time to wake up. In the evening, reducing exposure to artificial light, particularly from screens, can support the gradual release of melatonin, aiding in the transition to sleep.

Maintaining a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation, such as reading or gentle stretching, signals to the body that it's time to wind down. Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, can also contribute to better sleep quality. Additionally, creating a comfortable and dark sleep environment enhances the body's responsiveness to its natural circadian cues. Here's a summarized list of tips for resetting circadian rhythms:
Restoring your circadian rhythms can significantly improve sleep quality, mood, and overall well-being. Here are some tips to help restore your circadian rhythms:
-
Regular Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps stabilize your circadian rhythms.
-
Exposure to Light: In the morning, try to spend as much time as possible in natural light. Morning light helps "reset" your internal clock, signaling your body that it's time to be awake. Avoid bright light in the evening, especially from screens, as it can disrupt your biological clock.
-
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Try to avoid consuming caffeine in the afternoon and alcohol before bed. Both substances can disrupt sleep and disturb circadian rhythms.
-
Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: The temperature, noise level, and lighting in your bedroom should be conducive to quality sleep. The room should be dark, quiet, and cool.
-
Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes better sleep, but try to avoid intense workouts before bed, as they can energize you.
-
Relaxing Bedtime Rituals: Establish an evening routine that helps you unwind and prepare for sleep. This could include reading, meditation, or taking a warm bath.
-
Avoid Large Meals Before Bed: A heavy dinner or snack before bed can make it difficult to fall asleep. Try to finish eating 2-3 hours before bedtime.
-
Maintain a Consistent Body Temperature: Lowering your body temperature can help you fall asleep. A warm bath before bed can help, as your body naturally cools down afterward, promoting sleep.
-
Use Melatonin with Caution: If you have significant circadian rhythm issues, such as after crossing time zones, consider using melatonin, but it’s best to do so after consulting with a doctor.
-
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Avoid using your bed for work or other active tasks, except for sleep. This helps your body associate the bed exclusively with rest and sleep.
These tips can help you restore your circadian rhythms and improve your overall well-being.
Utilizing Light Therapy
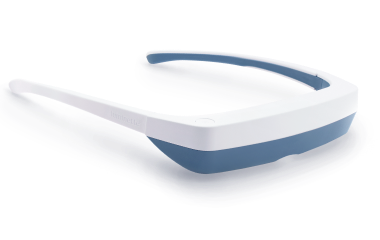
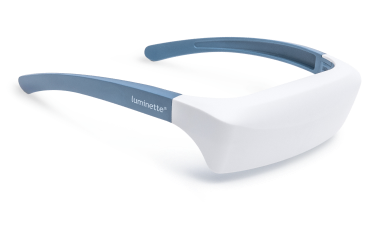
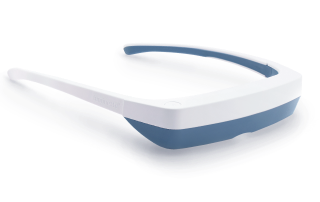
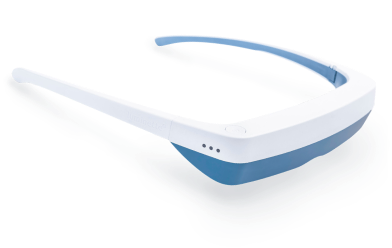
Utilizing light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is an effective method for resetting circadian rhythms and addressing disruptions. Light therapy involves exposure to a bright light that mimics natural sunlight, influencing the body's internal clock and helping regulate sleep-wake cycles. Light therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with seasonal mood swings, insomnia, or jet lag. Light therapy glasses, such as Luminette 3, offer a convenient and portable solution for incorporating light therapy into daily routines. These glasses provide a focused, adjustable light that can be worn while engaging in various activities, making them a practical choice for those seeking to optimize their circadian rhythms and improve overall sleep quality.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Lifestyle
Creating a sleep-friendly lifestyle is essential for supporting healthy circadian rhythms and improving overall sleep quality. One key aspect is maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This consistency reinforces the body's internal clock, promoting a more robust circadian rhythm. Prioritizing a relaxing bedtime routine can signal to the body that it's time to wind down, incorporating activities such as reading, gentle stretching, or meditation.

Additionally, cultivating a sleep-conducive environment is crucial. This involves keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet, minimizing disruptions that could interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle. Limiting screen time before bedtime and reducing exposure to blue light emitted by electronic devices can further support the body's natural production of melatonin, aiding in the transition to restful sleep. By incorporating these lifestyle practices, individuals can create a conducive environment for optimal sleep and promote the alignment of their circadian rhythms with the natural day-night cycle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining healthy circadian rhythms is integral to overall well-being and quality sleep. The intricate interplay of internal and external factors, including exposure to light, sleep habits, and lifestyle choices, underscores the importance of adopting practices that align with the body's natural internal clock. From establishing consistent sleep schedules to incorporating light therapy, individuals have a range of strategies to reset and support their circadian rhythms. Creating a sleep-friendly lifestyle, marked by consistent routines and conducive sleep environments, enhances the body's responsiveness to its natural circadian cues. By prioritizing these practices, individuals can foster better sleep quality, improved mood, and overall health, ultimately promoting a harmonious relationship with their circadian rhythms.
FAQ
What is a circadian rhythm, and why is it important?
A circadian rhythm is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and other physiological functions. It follows a 24-hour cycle and is influenced by external cues such as exposure to light. Maintaining healthy circadian rhythms is crucial for promoting quality sleep, supporting overall well-being, and regulating bodily processes.
How can I tell if my circadian rhythm is out of sync?
Signs that your circadian rhythm may be out of sync include difficulty falling or staying asleep at night, experiencing excessive tiredness or drowsiness during the day, and having irregular sleep patterns or consistently waking up at odd hours. These disruptions can affect your mood, concentration, and overall well-being.
What are common causes of circadian rhythm disruptions?
Circadian rhythm disruptions can be caused by factors such as shift work, which requires working at times that go against natural sleep cycles, and frequent travel across multiple time zones, leading to jet lag. Additionally, maintaining irregular sleep schedules, such as staying up late on weekends and waking up late, can hinder your body's ability to maintain a consistent internal clock.
How can light exposure help reset my circadian rhythm?
Exposure to natural light, especially in the morning, plays a crucial role in regulating your body's internal clock. Sunlight helps signal to your brain that it's time to wake up and be active, which can promote healthier sleep patterns. Spending time outdoors or near windows early in the day can help reinforce these natural cycles and improve sleep quality.
Can diet and exercise influence my circadian rhythm?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise can positively influence your circadian rhythm. Eating nutritious meals at consistent times can help stabilize your body's energy levels and support its natural cycles. Additionally, regular physical activity, particularly earlier in the day, can enhance your body's ability to fall asleep at night and regulate your sleep-wake cycle.









































 Please note
Please note