Chronobiology enables the study of the body’s behavior. Up until 2002, we were only able to distinguish two types of photoreceptors in the eye—cones (responsible for vision at night) and rods (responsible for vision during the day). In 2002, researchers made a discovery that enabled the increase of the field of practice of light therapy: in fact, a third type of photoreceptor exists, this time non-visual. Also known as ganglion pigment cells, these photoreceptors are involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms through the effect of light.
Light is much more than just what we rely on to see the world around us. It plays a crucial role in countless biological processes that govern our well-being. From regulating our sleep-wake cycles to influencing our mood and energy levels, light interacts with our bodies in profound ways. This blog post explores the multifaceted role light plays on the body, guided by insights and examples tailored for health enthusiasts, wellness seekers, and medical professionals alike.
The mechanism of light’s effect is made up of different stages
Light Penetration: Light enters the eye and activates the specialized ganglion pigment cells in the retina. These cells are sensitive to changes in light intensity and are crucial for regulating our body's response to light.
Signal Transformation: The photoreceptors within the eye, which include rods and cones, convert the incoming visual signal into an electrical signal. This process is essential for transmitting information about light to the brain. The electrical signal is then relayed through the optic nerve, which acts as a communication pathway, to our biological clock regulator, known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN).
Signal Interpretation and Hormonal Adjustment: The suprachiasmatic nucleus, located in the hypothalamus, interprets the electrical signal. This small but mighty part of the brain plays a crucial role in maintaining our daily rhythms. It communicates with the pineal gland to regulate hormone production. As a result, the gland adjusts the secretion levels of the sleep hormone melatonin and awake hormones such as cortisol, serotonin, and adrenaline. These hormones help synchronize our sleep-wake cycle with the external environment, aiding in overall health and well-being.
The Biological Effects of Light on the Body
Our bodies have evolved to be in sync with the natural rhythms of light and darkness. The 24-hour cycle, known as the circadian rhythm, controls many physiological processes such as hormone release, metabolism, and cell regeneration. Light is the primary cue that sets our internal clocks to this cycle. When we are exposed to natural light during the day, it signals our bodies to be awake and active. As the sun sets, dimmer artificial light or darkness triggers melatonin production, preparing us for sleep.
How Light Influences the Circadian Rhythm
The circadian rhythm is our body's natural clock, dictating the physiological processes that occur over a 24-hour cycle. Light exposure is a primary cue that helps regulate this internal clock. When light enters our eyes, it signals the brain to adjust our body's functions accordingly. Morning light prompts the production of serotonin, which boosts mood and focus, while evening darkness triggers melatonin production, preparing us for sleep.
Different types of light impact our circadian rhythm in varied ways. Natural sunlight aligns our internal clock with the day-night cycle, promoting synchronized bodily functions. In contrast, excessive exposure to artificial light, especially blue light from screens, can disrupt this rhythm, leading to sleep disturbances and related health issues. Understanding how light exposure affects the circadian rhythm is key to maintaining optimal health and well-being.
The Role of Light in Regulating Sleep-Wake Cycles
Our sleep-wake cycle is heavily influenced by light exposure. During the day, exposure to bright light helps keep us alert and awake. At night, the absence of light signals the body to wind down and prepare for sleep. This natural process works best when we follow a regular schedule, allowing for a smooth transition between sleeping and waking states.
Disruptions in light exposure, such as shift work or irregular sleeping patterns, can lead to altered sleep-wake cycles. Over time, these disruptions can contribute to sleep disorders like insomnia, making it difficult to achieve restful sleep. Incorporating healthy light habits, such as getting natural light exposure during the day and minimizing screen time before bed, can help regulate these cycles and improve overall sleep quality.
Light's Effect on Hormone Production (Melatonin and Cortisol)
Light plays a significant role in hormone regulation, particularly melatonin and cortisol. Melatonin, known as the "sleep hormone," is secreted in response to darkness, fostering a sense of calm and readiness for sleep. Conversely, cortisol, the "stress hormone," is influenced by morning light exposure, increasing alertness and energy.
The balance of these hormones is crucial for maintaining healthy physiological processes. Adequate light exposure during the day supports cortisol production, enhancing daytime performance, while dim lighting in the evening facilitates melatonin release, promoting restful sleep. Maintaining this hormonal balance is essential for overall well-being and can be achieved by aligning light exposure with natural day-night cycles.
Light's Influence on Mental and Emotional Health
Beyond regulating physiological processes, light also has a significant impact on our mental and emotional well-being. Exposure to natural sunlight triggers the release of serotonin, boosting mood and energy levels. In contrast, limited exposure to natural light or excessive exposure to artificial light can contribute to low mood and other disorders.
The Connection Between Light Exposure and Mood
Light exposure has a profound impact on our mood and emotional well-being. The presence of sunlight stimulates the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of happiness and positivity. Consequently, regular exposure to natural light can enhance mood, increase energy levels, and boost overall emotional health.
Conversely, limited access to daylight can lead to mood fluctuations and even contribute to mental health conditions. Seasonal mood swings, a type of disorder that occurs during the darker months, are a direct result of reduced sunlight exposure. Incorporating more natural light into our daily lives, whether through outdoor activities or simply spending time in well-lit spaces, can significantly improve mood and emotional well-being.
Light's Role in Managing Mood Swings and Anxiety
Beyond treating seasonal mood swings, light exposure also plays a role in managing general mood disorders and anxiety. Studies have shown that individuals exposed to more natural light experience reduced symptoms of mood swings and anxiety. This connection stems from light's influence on neurotransmitter regulation, particularly serotonin and dopamine.
Incorporating strategies to increase light exposure, such as spending time outdoors, utilizing light therapy, or creating bright indoor environments, can serve as complementary approaches to traditional treatments for depression and anxiety. These measures can help enhance mood stability and offer a non-invasive means to support mental health.
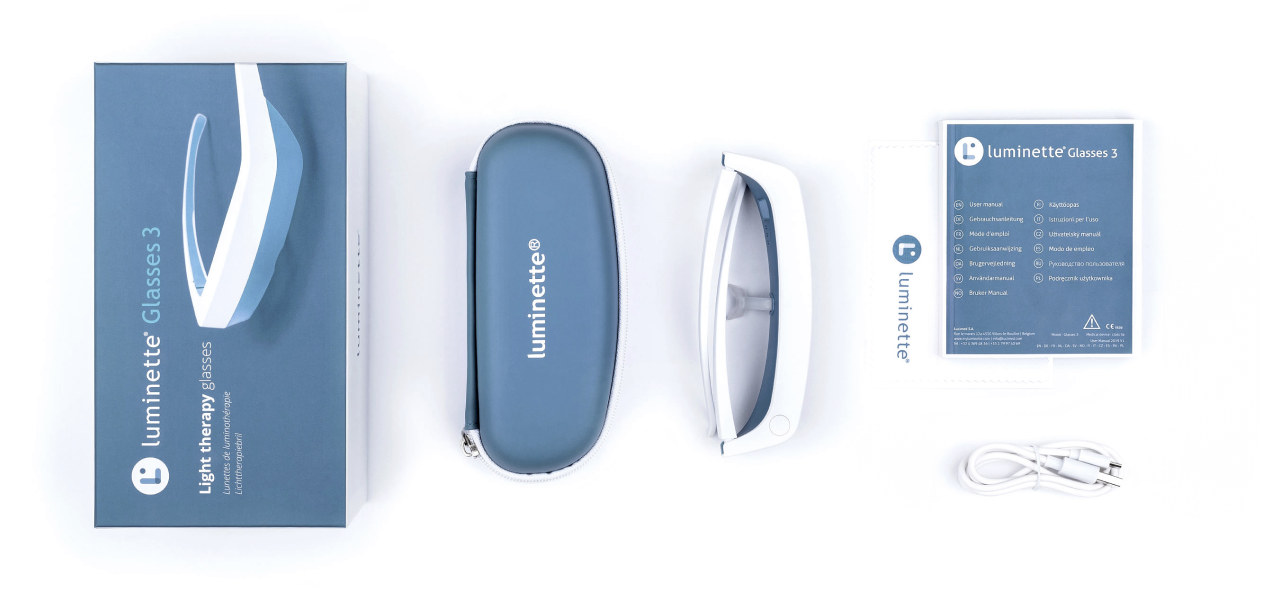
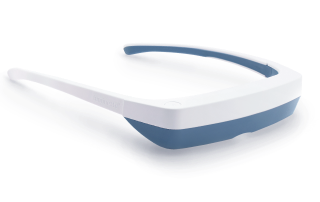
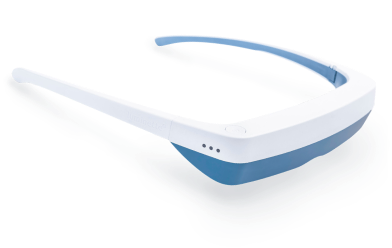
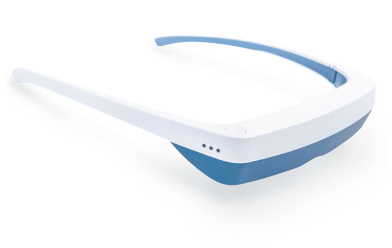
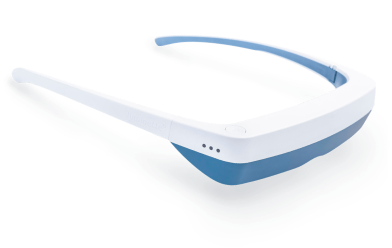
Luminette 3 light therapy glasses are innovative eyeglasses designed to allow you to enjoy a light therapy session while engaging in your regular activities. Unlike traditional therapy lamps, Luminette 3 eyeglasses feature an artificial light source that directs a safe light beam into your eyes without causing any dazzling effect or obstructing your clear vision.
To use them, simply wear the eyeglasses and press a button to activate the light, and your phototherapy session begins. These glasses are user-friendly and compatible with those who wear prescription glasses or contact lenses, ensuring no disruption to vision or comfort.
With the convenience of Luminette 3, there is no longer a need to sit beside a stationary light therapy lamp for 30 minutes each day. The freedom to move around means you can prepare breakfast, dive into a captivating book, catch up on your favorite TV shows, work on your computer tasks, or even engage in light exercises, all while receiving your therapeutic light exposure. Whether you're at home or on the go, Luminette 3 offers a flexible and efficient solution to incorporate light therapy into your daily life.
The Impact of Light on Physical Health
Light's effect on our physical health goes beyond sleep and mood regulation. Research has shown that exposure to natural light offers numerous benefits for our physical well-being, from boosting vitamin D levels to supporting immune function.
How Light Affects Vitamin D Synthesis
One of the most well-known roles of light in physical health is its involvement in vitamin D synthesis. When the skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from sunlight, it initiates the production of vitamin D, a crucial nutrient for bone health, immune function, and overall vitality.
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to various health issues, including weakened bones, compromised immunity, and an increased risk of chronic diseases. Ensuring adequate sun exposure, while taking care to avoid overexposure, is key to supporting optimal vitamin D levels. For those in regions with limited sunlight, vitamin D supplements may be necessary to maintain adequate levels and support overall health.
Light Exposure and Eye Health
Light exposure also has implications for eye health. While natural light is essential for maintaining visual acuity and overall eye function, excessive exposure, particularly to artificial light sources, can lead to eye strain and digital eye fatigue. Prolonged screen use without adequate breaks can contribute to discomfort and vision-related issues.
To protect eye health, it's important to practice good visual hygiene. This includes taking regular breaks from screens, using blue light filters, and ensuring adequate lighting in our environments. Additionally, spending time outdoors and allowing the eyes to adapt to natural light can promote eye health and reduce the risk of vision-related problems.
The Influence of Light on Energy Levels and Fatigue
Light exposure significantly impacts our energy levels and susceptibility to fatigue. Exposure to natural light during the day helps increase alertness and cognitive performance, while a lack of light can lead to fatigue and diminished productivity. This is particularly relevant in office environments, where artificial lighting may not provide the same energizing effect as natural light.
Optimizing light exposure throughout the day can enhance energy levels and combat fatigue. Simple strategies, such as taking breaks outside, working near windows, or using light therapy devices, can make a noticeable difference in maintaining high energy levels and reducing the midday slump. Prioritizing natural light exposure is a simple yet effective way to boost vitality and overall well-being.
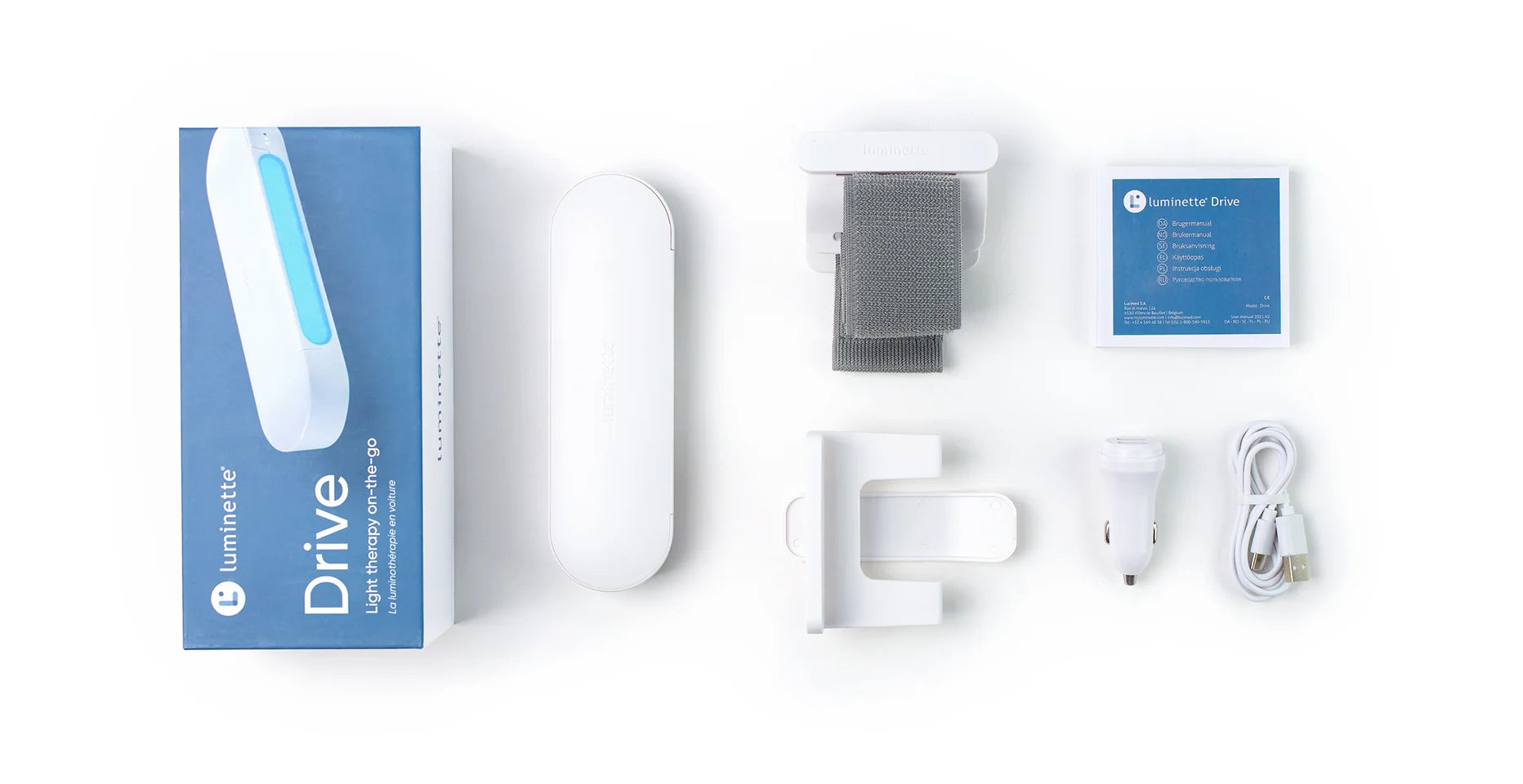
Light Therapy Lamp Drive is an innovative light therapy lamp designed for busy individuals, allowing you to conveniently conduct your phototherapy session while on the road. This device is ingeniously crafted to attach seamlessly to the sun visor of your vehicle. With a simple flip of a switch, it provides an effective light therapy session as you drive to your destination.
For those who find themselves spending at least 20 minutes behind the wheel each day, Drive is a perfect companion, offering a unique solution to integrate wellness into your daily routine. This is especially advantageous for individuals who embark on long night drives, as it helps to counteract the effects of darkness and fatigue.
Drive emits a safe, bright light into your eyes, meticulously designed to enhance your alertness without interfering with your driving. By doing so, it delivers the full spectrum of light therapy benefits, which include regulating the production of melatonin, the sleep-inducing hormone, thereby promoting a state of wakefulness and heightened alertness. This makes it not only a functional tool but also a valuable ally in maintaining your overall well-being and mental sharpness during your travels.
Benefits of Light Therapy
Light therapy offers numerous benefits beyond treating mood disorders, making it a versatile tool for enhancing health and well-being. Initially developed for seasonal mood swings, its uses have grown over the years.
Research highlights that light therapy can improve sleep quality by regulating sleep patterns, especially for those with insomnia or irregular schedules. It is particularly impactful for jet lag and shift work-related sleep disturbances. By exposing individuals to controlled doses of bright light, light therapy helps reset the body’s internal clock, promoting better sleep hygiene and aligning sleep-wake cycles with natural circadian rhythms. This alignment boosts energy levels and overall health.
Additionally, light therapy is beneficial for cognitive performance. Studies suggest that exposure to bright light during the day enhances focus, attention, and memory. These cognitive benefits are especially valuable for people in demanding work environments or those aiming to optimize their mental abilities. Improved productivity and problem-solving skills make light therapy appealing for personal and professional growth.
Furthermore, ongoing research explores light therapy’s potential in mood stability and supporting individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome. As we continue to uncover its effects, light therapy is poised to become a key component of holistic health care strategies.
Discover what role light plays on the body
with Roland Pec - sleep specialist and chrono-therapist









































 Please note
Please note