Terwijl andere vitamines voornamelijk via voeding worden verkregen, kan het lichaam vitamine D aanmaken wanneer de huid wordt blootgesteld aan zonlicht. Dus tijdens de winter, wanneer er minder zon is, produceert het lichaam minder vitamine D. Dit kan leiden tot een vitamine D-tekort en problemen veroorzaken zoals spierzwakte, botpijn en een verhoogd risico op breuken.
Om deze reden zou je je met het naderen van de winterdagen niet alleen zorgen moeten maken over de kou, maar ook over hoe je voldoende vitamine D-niveaus zult behouden. Hier komen lichttherapiebrillen om de hoek kijken!
Dit artikel bespreekt het belang van vitamine D, hoe lichttherapie je kan helpen deze vitamine in de winterdagen binnen te krijgen, en andere manieren om je niveaus gezond te houden gedurende de koude, donkere winter.
Wat is vitamine D?
Vitamine D is een in vet oplosbare voedingsstof die een cruciale rol speelt in verschillende lichaamsfuncties, waardoor het essentieel is voor je algehele gezondheid. Het is misschien het best bekend om zijn bijdrage aan de gezondheid van de botten, omdat het het lichaam helpt calcium en fosfor op te nemen, die cruciaal zijn voor het behouden van sterke en gezonde botten. Daarnaast is vitamine D ook van vitaal belang voor het ondersteunen van een robuust immuunsysteem, het helpen voorkomen van ziekten en zelfs het bevorderen van stemmingsregulatie door het risico op depressie en andere stemmingsstoornissen te verminderen.
Deze belangrijke vitamine komt slechts in een paar voedingsmiddelen voor, zoals vette vis (zalm, makreel, tonijn), eidooiers en verrijkte producten zoals melk, ontbijtgranen en sinaasappelsap. Alleen op voeding vertrouwen om aan je vitamine D-behoefte te voldoen kan echter een uitdaging zijn, vooral in seizoenen met beperkte blootstelling aan zonlicht. Gelukkig kan onze huid van nature vitamine D aanmaken wanneer deze wordt blootgesteld aan direct zonlicht. Daarom wordt vitamine D vaak de zonneschijnvitamine genoemd, wat de directe verbinding met blootstelling aan zonlicht benadrukt.
Voor veel mensen vereist het waarborgen van voldoende vitamine D-niveaus een combinatie van blootstelling aan zonlicht, voeding en af en toe supplementen. In de winter kunnen innovatieve oplossingen zoals lichttherapiebrillen ook een belangrijke rol spelen bij het overbruggen van het tekort en het optimaal laten functioneren van je lichaam.

Voordelen van vitamine D
Ondersteunt de gezondheid van de botten
Een van de belangrijkste functies van vitamine D is de opname van calcium. Vitamine D helpt het lichaam calcium op te nemen, wat nodig is voor botmineralisatie en sterkte.
Dit betekent dat zonder voldoende vitamine D je lichaam calcium niet goed kan opnemen, wat leidt tot verzwakte botten. Bij kinderen kan dit rachitis (botmisvormingen) veroorzaken. Bij volwassenen kan het osteomalacie (verzachting van de botten) en osteoporose (broze, poreuze botten) veroorzaken, wat het risico op breuken verhoogt.
Ondersteunt het immuunsysteem
Vitamine D beïnvloedt direct de functie van verschillende immuuncellen. Het verbetert bijvoorbeeld het vermogen van macrofagen om ziekteverwekkers op te nemen en te verteren.
Dus, vermindert vitamine D-tekort de immuunrespons, terwijl adequate vitamine D-niveaus het immuunsysteem helpen reguleren en het voor je lichaam gemakkelijker maken om infecties te bestrijden en het risico op auto-immuunziekten zoals type I diabetes, reumatoïde artritis en multiple sclerose te verminderen.
Helpt de stemming te reguleren
Vitamine D is betrokken bij de synthese van serotonine, een neurotransmitter die stemming, geluk en slaap reguleert. Als gevolg hiervan worden lage vitamine D-niveaus geassocieerd met stemmingsstoornissen, zoals gevoelens van diepe droefheid die vaak voorkomen in de wintermaanden wanneer zonlicht beperkt is. Het handhaven van adequate vitamine D-niveaus is belangrijk voor het voorkomen en behandelen van stemmingsstoornissen.
Ondersteunt spierfunctie
Vitamine D helpt ons lichaam calcium op te nemen, wat essentieel is voor spiercontractie. Daarnaast helpt vitamine D spiervoorlopercellen (myocyten) zich te ontwikkelen tot volwassen spiervezels. Dus, optimaliseert vitamine D spierkracht en prestaties, terwijl onvoldoende niveaus de ontwikkeling en groei van spiervezels kunnen belemmeren, wat leidt tot spierzwakte.
Dit vind je misschien ook leuk: Geeft vitamine D je energie: Vitamine D en vermoeidheid.

Symptomen van vitamine D-tekort
-
Vermoeidheid en zwakte: Een tekort aan vitamine D kan ervoor zorgen dat je je de hele tijd moe voelt, zelfs na een verkwikkende nachtrust.
-
Bots- en spierzwakte: Vitamine D is belangrijk voor gezonde botten; lage niveaus kunnen verzwakte botten veroorzaken, wat leidt tot botpijn, gewrichtspijn en spierzwakte.
-
Stemmingswisselingen: Omdat vitamine D betrokken is bij de productie van serotonine die de stemming reguleert, kunnen lage vitamine D-niveaus stemmingswisselingen veroorzaken, vooral gevoelens van diepe droefheid tijdens de winter.
-
Frequent ziek zijn: Vitamine D ondersteunt het immuunsysteem en versterkt het vermogen van ons lichaam om ziektes te bestrijden. Bij een tekort aan deze vitamine neemt de immuunfunctie over het algemeen af, wat leidt tot vaker verkoudheden en infecties.
- Haaruitval: Vitamine D reguleert de haarfollikelcyclus, vooral in de groeifase wanneer haarzakjes nieuw haar laten groeien. Een tekort of onvoldoende vitamine D beïnvloedt dus de ontwikkeling van gezond haar, wat leidt tot dunner wordend haar of haaruitval.
Personen met een risico op vitamine D-tekort
-
Oudere volwassenen: Veroudering beïnvloedt onze huid, waardoor deze minder efficiënt wordt in het stimuleren van de productie van vitamine D uit zonlicht. Bovendien brengen oudere volwassenen meer tijd binnenshuis door, wat de blootstelling aan zonlicht voor de productie van vitamine D vermindert.
-
Mensen met een donkere huid: Mensen met een donkere huid hebben meer melanine, wat het vermogen van de huid vermindert om vitamine D uit zonlicht te produceren.
-
Mensen met beperkte blootstelling aan zonlicht: Wanneer mensen het grootste deel van hun tijd binnenshuis doorbrengen (vanwege hun levensstijl, werk of gezondheidsproblemen), krijgen ze niet genoeg zonlicht om voldoende vitamine D aan te maken.
-
Mensen die het grootste deel van hun lichaam bedekken: Hoe meer huid bedekt is met kleding, hoe minder UVB-straling het lichaam ontvangt voor de productie van vitamine D. Daarom lopen vrouwen in islamitische gemeenschappen die bescheidenheid of religieuze kledingvoorschriften volgen een hoger risico op vitamine D-tekort.
-
Mensen die in noordelijke breedtegraden wonen: De zon is zwakker in gebieden verder van de evenaar. Daardoor hebben mensen in Canada of delen van het noorden van de VS een hoger risico op vitamine D-tekort. Hoewel het niet heel ver naar het noorden is, ligt het VK nog steeds op een breedtegraad waar de hoek van de zon in de winter de effectiviteit van UVB-stralen voor vitamine D-productie vermindert. Dus ook mensen in het VK lopen risico op een vitamine D-tekort.
- Obese personen. Vitamine D is vetoplosbaar, wat betekent dat het wordt opgeslagen in vetweefsel. Bij mensen met een hoger vetpercentage raakt meer vitamine D gevangen in vetweefsel, en is er minder beschikbaar voor gebruik door het lichaam, wat een tekort veroorzaakt.
Hoe je op natuurlijke wijze vitamine D kunt krijgen
-
Blootstelling aan zonlicht: Ga vaker naar buiten en krijg natuurlijk zonlicht, want onze huid produceert vitamine D wanneer deze aan zonlicht wordt blootgesteld. Sterker nog, wanneer er veel zonlicht is, kan ons lichaam voldoende vitamine D aanmaken. Specifiek, wanneer 22% van de onbedekte huid 10–15 minuten zonlicht krijgt tijdens de zomer of lente (wanneer er veel zonlicht is), kan het lichaam tot 1.000 IE vitamine D produceren.
- Dieet: Neem veel vitamine D-rijke voeding op in je dieet, zoals vette vis en eierdooiers.
Effectieve methoden om vitamine D in de winter binnen te krijgen
Zonlicht is niet sterk genoeg voor voldoende vitamine D-productie tijdens de kortere, donkerdere dagen van de winter. Dus naarmate we van de zomer via de herfst naar de winter gaan, produceert ons lichaam minder vitamine D door zonlicht. Hierdoor kunnen we een vitamine D-tekort krijgen en de gezondheidsrisico’s die daarmee gepaard gaan, tenzij we deze vitamine uit andere bronnen kunnen halen.
Voedingsbronnen van vitamine D
Hoewel er maar weinig voedingsbronnen van vitamine D zijn, kan het eten van deze voedingsmiddelen gedurende de winter je helpen voldoende hoeveelheden binnen te krijgen tijdens de koude, donkere maanden waarin er weinig zonlicht is voor de aanmaak van vitamine D.
Overweeg om van november tot maart minstens twee porties vette vis (zoals zalm) per week te eten. Als je vegetariër bent, drink dan minstens 3 kopjes verrijkte plantaardige melk (zoals amandel-, soja- of havermelk) per week.
Vitamine D supplementen: Dosering en veiligheid
Vitamine D3-supplementen zijn zeer effectief in het verhogen van de vitamine D-spiegel in het bloed. Daarom helpt het dagelijks innemen van een vitamine D-supplement gedurende de wintermaanden om gezonde niveaus te behouden.
De juiste dosering van vitamine D hangt af van de leeftijd en gezondheidstoestand van de persoon.
Volgens het National Institute of Health varieert de hoeveelheid vitamine D die je nodig hebt afhankelijk van de leeftijd als volgt:
|
Levensfase |
Aanbevolen hoeveelheid |
|
Baby (0-12 maanden) |
400 IU (10 mcg) |
|
Kinderen (1-13 jaar) |
600 IU (15 mcg) |
|
Tieners (14-18 jaar) |
600 IU (15 mcg) |
|
Volwassenen (19-70 jaar) |
600 IU (15 mcg) |
|
Oudere volwassenen (71 jaar en ouder) |
800 IU (20 mcg) |
|
Zwangere en zogende vrouwen |
600 IU (15 mcg) |
Supplementen zijn over het algemeen veilig om de vitamine D-spiegel tijdens de winter op peil te houden. Je moet echter voorzichtig zijn met het innemen van vitamine D-supplementen omdat ze meestal zeer krachtig zijn. Sommige bevatten tot 10.000 IU vitamine D, en langdurig gebruik kan gemakkelijk leiden tot toxiciteit.

Lichttherapie voor vitamine D
Omdat beperkte blootstelling aan zonlicht de belangrijkste oorzaak is van een tekort aan vitamine D in de winter, kan blootstelling aan fel licht dat zonlicht nabootst helpen. Gespecialiseerde zontherapielampen en apparaten zenden fel licht uit met dezelfde golflengte en intensiteit als de zon om je lichaam te helpen vitamine D op natuurlijke wijze aan te maken tijdens de winter.
Stel jezelf elke ochtend in de winter bloot aan dit zonnabootsend licht, en je lichaam zal voldoende vitamine D aanmaken zonder zorgen over toxiciteit.
Dit vind je misschien ook leuk: Voordelen van zonlicht en hoe lichttherapie kan helpen.
Overzicht van lichttherapie
Lichttherapie is een vorm van behandeling waarbij kunstlicht wordt gebruikt om natuurlijk zonlicht na te bootsen om het lichaam te misleiden zodat het denkt dat het zonlicht ontvangt, waardoor de gunstige effecten van zonlicht worden geproduceerd.
Hoe helpt lichttherapie bij de aanmaak van vitamine D?
Lichttherapie gebruikt speciale apparaten om fel licht uit te stralen met dezelfde intensiteit als natuurlijk zonlicht. Wanneer het lichaam aan dit kunstlicht wordt blootgesteld, denkt het dat het natuurlijk zonlicht is, waardoor het zich gedraagt zoals het zou doen bij blootstelling aan natuurlijk zonlicht.
Standaard lichttherapie verhoogt echter de aanmaak van vitamine D niet, omdat het niet het type licht uitstraalt dat voor dit proces nodig is.
De aanmaak van vitamine D in de huid wordt geactiveerd door UVB-straling in zonlicht. Helaas gebruiken standaard lichttherapieapparaten fel wit of blauw licht, die geen UVB-stralen bevatten. Hierdoor kunnen deze standaardapparaten de andere voordelen van zonlicht bieden (zoals het reguleren van de slaap-waakcyclus en het verbeteren van de stemming), maar kunnen ze de aanmaak van vitamine D niet stimuleren.
Voor lichttherapie die de aanmaak van vitamine D stimuleert, heb je speciale lichttherapielampen nodig die UVB-stralen uitstralen. Wanneer je lichaam aan licht wordt blootgesteld, dringen de UVB-stralen door je huid, reageren ze met een verbinding genaamd 7-dehydrocholesterol en produceren ze vitamine D.
De speciale UVB-uitstralende lampen bootsen het natuurlijke proces van vitamine D-synthese na dat plaatsvindt wanneer de huid wordt blootgesteld aan zonlicht. Je kunt deze UVB-lichttherapielampen thuis gebruiken tijdens de koude winterdagen om het natuurlijke zonlicht te compenseren en een consistente aanmaak van vitamine D te garanderen. Zet gewoon de lamp aan en hij zal stralingsenergie van de juiste UV-golflengte en intensiteit uitstralen, waardoor de aanmaak van vitamine D in je huid wordt gestimuleerd.
Lees ook: Beste lichttherapielampen: hoe te kiezen.
Soorten lichttherapieapparaten
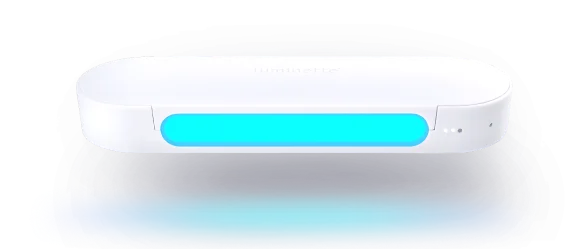
Paneelstijl lichttherapielamp
Dit zijn grote en lompe lichtboxen die zonlicht nabootsend fel licht uitstralen voor lichttherapie. Ze hebben grote oppervlakken, waardoor ze meer licht kunnen uitstralen dan andere lichttherapielampen.
Ze geven ook de vereiste lichtintensiteit voor de aanmaak van vitamine D (10.000 lux) af vanaf de verste afstanden (tot 50 cm). Dit stelt je in staat om op een aanzienlijke afstand van de lamp te zitten tijdens je lichttherapiesessie.
Je kunt echter niet rondlopen tijdens je sessie. En het formaat van deze lampen maakt ze onhandig voor reizen.
Compacte lichttherapielampen
Compacte lichttherapielampen zijn relatief klein. Door hun kleine formaat is hun lichtcapaciteit zwakker, maar het blauwe deel van het spectrum is meestal verrijkt, waardoor ze hetzelfde effect hebben als witte lichtlampen.
Deze lampen zijn beter geschikt voor reizen. En ze nemen niet te veel ruimte in op je tafelblad. Net als paneelstijl lampen zijn compacte lampen echter nog steeds onbeweeglijk, dus je kunt niet rondlopen tijdens je lichttherapiesessie. Sterker nog, je moet niet alleen bij de lamp zitten tijdens je lichttherapiesessies, maar je moet ook hoofdbewegingen beperken omdat het licht zwakker is.
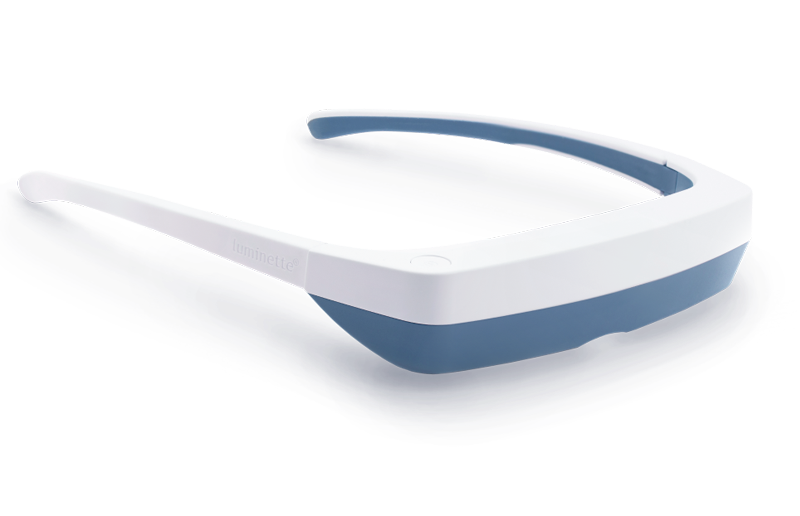
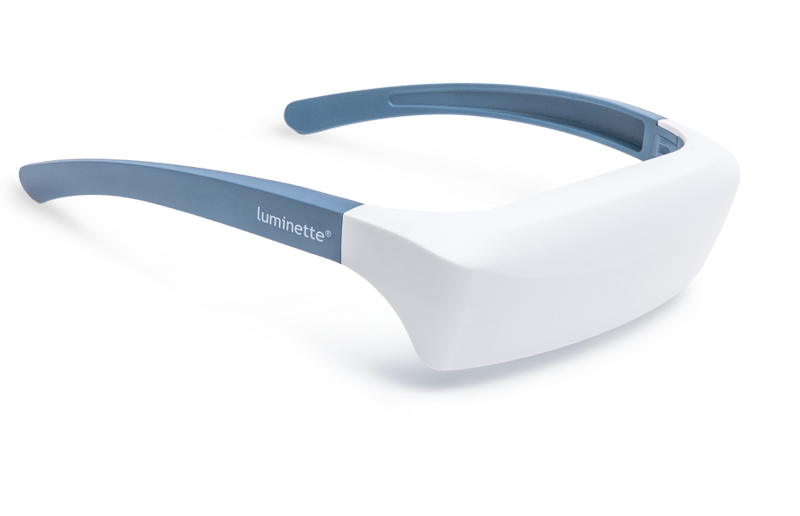
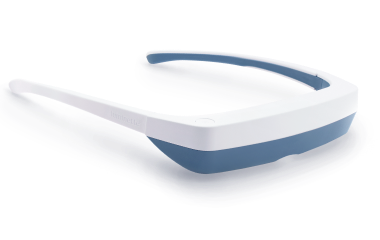
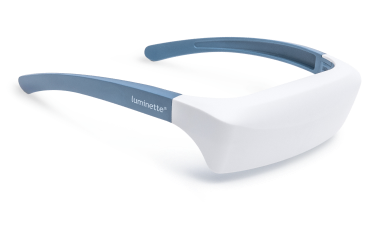
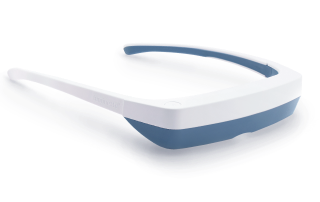
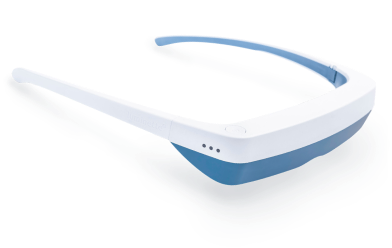
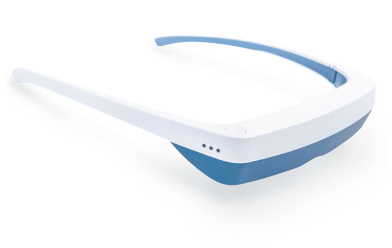
Lichttherapiebrillen
Lichttherapiebrillen (ook bekend als vizieren) zijn lichttherapie “lampen” die ontworpen zijn om als bril te worden gedragen voor een meer gekalibreerde lichttherapiebehandeling.
Een lichtbron is gemonteerd bovenop de bril, zodat wanneer je ze draagt, het apparaat zonnabij licht direct in je ogen stuurt. Zelfs wanneer je je hoofd draait en beweegt tijdens je lichttherapiesessies, blijft het licht op dezelfde afstand van je ogen, wat optimale lichttherapieresultaten garandeert.
Lichttherapiebrillen zijn perfect voor mensen die liever niet stilzitten bij een lamp voor lichttherapie. Met lichttherapiebrillen kun je je normale routine voortzetten tijdens je lichttherapiesessies.
Hoe gebruik je een lichttherapie-apparaat
- Kies het juiste lichttherapie-apparaat: Zorg ervoor dat het lichttherapie-apparaat dat je kiest tot 10.000 lux licht uitstraalt (want dat is de lichtintensiteit die de natuurlijke productie van vitamine D in de huid kan stimuleren). Zorg er bij het kiezen van lichttherapie-apparaten voor vitamine D voor dat het apparaat UVB-stralen uitzendt.
-
Positioneer het licht op de juiste manier: Positioneer de lamp 40 - 60 cm (16 - 24 inch) van je gezicht. Kijk niet direct in het licht, maar zorg ervoor dat je ogen eraan worden blootgesteld. Wanneer je kiest voor lichttherapiebrillen voor winterdepressie, draag je ze gewoon en hoef je je geen zorgen te maken over het correct positioneren van het apparaat.
-
Gebruik elke ochtend minstens 30 minuten: Elke lichttherapiesessie moet tussen de 20 en 30 minuten duren. Consistentie is ook belangrijk. Zorg ervoor dat je het apparaat elke dag gedurende de winterdagen gebruikt. En het is het meest effectief om het licht vroeg in de ochtend te gebruiken, bij voorkeur na het wakker worden.
Tips om de opname van vitamine D te maximaliseren
Breng tijd buiten door: Breng indien mogelijk wat tijd buiten door tijdens daglichturen. Hoewel de zon misschien niet zo sterk is, kan blootstelling aan natuurlijk licht (zelfs in kleine doses) nog steeds helpen bij je vitamine D-inname.
Maximaliseer blootstelling van de huid: Hoe meer huid blootgesteld wordt aan zonlicht of zonnabij licht van UVB-lampen, hoe meer vitamine D je lichaam kan produceren. Probeer je armen, benen en gezicht aan het licht bloot te stellen.
Vermijd zonnebrandcrème: Zonnebrandcrème blokkeert UVB-stralen, die het lichaam gebruikt voor de productie van vitamine D. Om de productie van vitamine D te maximaliseren, breng tijd door in de zon of onder zonnabij licht zonder zonnebrandcrème.
Neem vitamine D met gezonde vetten: Vitamine D is vetoplosbaar, wat betekent dat het beter wordt opgenomen wanneer het wordt geconsumeerd met voedingsvetten. Neem daarom vitamine D-rijke voedingsmiddelen of vitamine D-supplementen samen met maaltijden die gezonde vetten bevatten (zoals avocado, olijfolie of vette vis).
Behaal een gezond gewicht: Vitamine D wordt opgeslagen in vetcellen. Overgewicht houdt vitamine D vast, waardoor je meer nodig hebt om voldoende niveaus te behouden. Maar met een gezond gewicht heb je minder nodig om adequate niveaus te behouden.
Conclusie
Bestel de innovatieve Luminette 3. Ons lichaam maakt het grootste deel van de benodigde vitamine D aan uit zonlicht. Het is dus een uitdaging om voldoende vitamine D binnen te krijgen in de winter wanneer er minder zonlicht is.
Gelukkig kan lichttherapie het beperkte zonlicht in de winter compenseren. Lichttherapie met speciale lampen die stralingsenergie van geschikte UV-golflengten en intensiteit uitstralen, kan de productie van vitamine D in de huid stimuleren.
Standaard lichttherapieapparaten kunnen je ook helpen winterdepressie te behandelen, de focus en productiviteit te verbeteren, de stemming en mentale gezondheid te versterken, de slaap te verbeteren en jetlag te bestrijden. De beste standaard lichttherapieapparaten zijn vizieren (lichttherapiebrillen). In tegenstelling tot gewone lichttherapielampen maken vizieren lichttherapie onderweg mogelijk. Je draagt ze als gewone bril en ze sturen zonlichtnabootsend licht direct in je ogen voor een meer geijkte en effectieve behandeling.
De Luminette 3 is de beste lichttherapiebril die je zult vinden. Ze zijn lichtgewicht en hebben een verstelbare ergonomische neussteun, waardoor ze supercomfortabel zijn. Klaar om je op je best te voelen tijdens de koude winterdagen?
Veelgestelde vragen
Wat is het beste type lichttherapieapparaat voor de productie van vitamine D?
Lichttherapieapparaten voor de productie van vitamine D moeten fel licht uitstralen met dezelfde golflengte en intensiteit als zonlicht. Omdat het UVB-stralen in zonlicht zijn die de huid gebruikt om vitamine D te produceren, moeten lichttherapielampen voor vitamine D UVB-stralen uitstralen. De lichtintensiteit moet ook minstens 10.000 lux zijn.
Hoe lang moet ik een lichttherapieapparaat gebruiken?
Hoe lang je een lichttherapieapparaat gebruikt, hangt af van wat je ermee wilt behandelen. Bij het gebruik van lichttherapie om vitamine D te krijgen tijdens de winter, gebruik je het apparaat elke dag gedurende de koude, donkere maanden.
Is lichttherapie veilig voor iedereen?
Kan ik te veel vitamine D krijgen door lichttherapie?
Je kunt niet te veel vitamine D krijgen die natuurlijk in je lichaam wordt geproduceerd door blootstelling aan zonlicht of zonlichtnabootsend licht van lichttherapieapparaten. Wanneer je voldoende vitamine D hebt, zal je lichaam gewoon minder produceren. Het gebruik van lichttherapie om vitamine D te krijgen stelt je lichaam dus in staat om zoveel te produceren als het nodig heeft zonder het risico op toxiciteit.
Kan ik lichttherapie gebruiken om andere aandoeningen te behandelen dan een vitamine D-tekort?
Je kunt lichttherapie gebruiken om een reeks seizoensgebonden stemmingsstoornissen te behandelen (inclusief winterdepressie) en verstoringen van de interne klok van het lichaam (als gevolg van ploegendiensten of snel reizen over meerdere tijdzones).








































 Please note
Please note